線性表的本質(zhì)、操作及順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu)(六)-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
我們說到線性表,可能好多人還不太理解。那么我們舉個例子來說,在幼兒園中,老師們總會讓小朋友以同樣的派對秩序出行,這個例子的本質(zhì)就是線性表。

那么線性表(List)的表現(xiàn)形式是怎樣的呢?符合以下幾個特征:1、零個或多個數(shù)據(jù)元素組成的集合;2、數(shù)據(jù)元素在位置上是有序排列的;3、數(shù)據(jù)元素的個數(shù)是有限的;4、數(shù)據(jù)元素的類型必須是相同的。那么線性表的抽象定義是怎么定義的呢?線性表是具有相同類型的 n( ≥ 0 ) 個數(shù)據(jù)元素的有限序列。如下
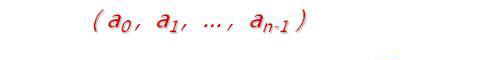
下來我們來看看 List 的本質(zhì):1、a0為線性表的第一個元素,只有一個后繼;2、an-1為線性表的最后一個元素,只有一個前驅(qū);3、除 a0和 an-1外的其他元素 ai,既有前驅(qū)又有后繼;4、直接支持逐項訪問和順序存取。下面我們來看看線性表一些常用操作:a> 將元素插入線性表;b> 將元素從線性表中刪除;c>獲取目標(biāo)位置處元素的值;d>設(shè)置目標(biāo)位置處元素的值;d> 獲取線性表的長度;e>清空線性表。
線性表在程序中表現(xiàn)為一種特殊的數(shù)據(jù)類型。定義如下
#ifndef LIST_H
#define LIST_H
#include "Object.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T >
class List : public Object
{
public:
List() {}
virtual bool insert(const T& e) = 0;
virtual bool insert(int i, const T& e) = 0;
virtual bool remove(int i) = 0;
virtual bool set(int i, const T& e) = 0;
virtual bool get(int i, T& e) const = 0;
virtual int length() const = 0;
virtual void clear() = 0;
};
}
#endif // LIST_H下面我們來看看順序存儲的定義:線性表的順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu),指的是用一段地址連續(xù)的存儲單元依次存儲線性表中的數(shù)據(jù)元素。如下
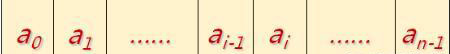
那么我們該如何設(shè)計呢?可以使用一維數(shù)組來實現(xiàn)順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu),存儲空間:T* m_array;當(dāng)前長度: int m_length;定義如下
template < typename T >
class SeqList : public List<T>
{
protected:
T* m_array;
int m_length;
////
}那么順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu)的元素獲取操作怎樣來實現(xiàn)呢?一是判斷目標(biāo)位置是否合法,二是將目標(biāo)位置作為數(shù)組下標(biāo)獲取元素。定義如下
bool SeqList<T>::get(int i, T& e) const
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
e = m_array[i];
}
return ret;
}順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu)的元素插入示例如下
bool SeqList<T>::insert(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length));
ret = ret && (m_length < capacity());
if( ret )
{
for(int p=m_length-1; p>=i; p--)
{
m_array[p+1] = m_array[p];
}
m_array[i] = e;
m_length++;
}
return ret;
}順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu)的元素刪除操作:1、判斷目標(biāo)位置是否合法;2、將目標(biāo)位置后的所有元素前移一個位置;3、線性表長度減一。刪除示例如下
bool SeqList<T>::remove(int i)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
for(int p=i; p<m_length-1; p++)
{
m_array[p] = m_array[p+1];
}
m_length--;
}
return ret;
}我們完成了以上的幾個重要操作之后,我們來看看 SeqList 處于一個什么樣的位置,如下圖所示
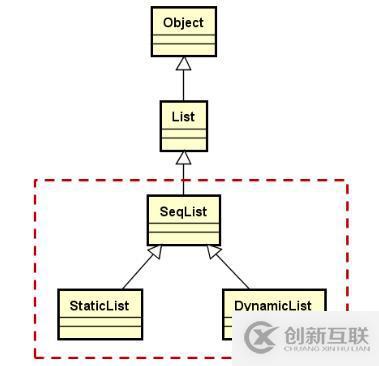
那么這便是一個順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu)線性表的抽象實現(xiàn)了。在 SeqList 設(shè)計時,我們要只有以下幾點:1、抽象類模板,存儲空間的位置和大小由子類完成;2、實現(xiàn)順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu)線性表的關(guān)鍵操作(增、刪、查等);3、提供數(shù)組操作符,方便快速獲取元素。那么它的抽象定義如下:
template < typename T >
class SeqList : public List<T>
{
protected:
T* m_array; // 順序存儲空間
int m_length; // 當(dāng)前線性表長度
public:
bool insert(int i, const T& e);
bool remove(int i);
bool set(int i, const T& e);
bool get(int i, T& e) const;
int length() const;
void clear();
// 順序存儲線性表的數(shù)組訪問方式
T& operator[] (int i);
T& operator[] (int i) const;
// 順序存儲空間的容量
virtual int capacity() const = 0;
};下來我們來看看 SeqList 是怎么寫的
SeqList.h 源碼
#ifndef SEQLIST_H
#define SEQLIST_H
#include "List.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T >
class SeqList : public List<T>
{
protected:
T* m_array;
int m_length;
public:
bool insert(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length));
ret = ret && (m_length < capacity());
if( ret )
{
for(int p=m_length-1; p>=i; p--)
{
m_array[p+1] = m_array[p];
}
m_array[i] = e;
m_length++;
}
return ret;
}
bool insert(const T& e)
{
return insert(m_length, e);
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
for(int p=i; p<m_length-1; p++)
{
m_array[p] = m_array[p+1];
}
m_length--;
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
m_array[i] = e;
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int i, T& e) const
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length));
if( ret )
{
e = m_array[i];
}
return ret;
}
int length() const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
m_length = 0;
}
T& operator[] (int i)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
return m_array[i];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
}
T operator[] (int i) const
{
return (const_cast<SeqList<T>&>(*this))[i];
}
virtual int capacity() const = 0;
};
}
#endif // SEQLIST_Hmain.cpp 源碼
#include <iostream>
#include "Seqlist.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
int main()
{
SeqList<int>* l;
return 0;
}經(jīng)過編譯,編譯時通過的,說明我們已經(jīng)完成了 SeqList 抽象類的實現(xiàn)了。接下來我們思考下,在前面的 SeqList 的實現(xiàn)中,我們在它的下面還有 StaticList 和 DynamicList 的兩個子類,那么我們該如何去實現(xiàn)它們呢?StaticList 和 DynamicList 的差異在哪里?是否可以將 DynamicList 作為 StaticList 的子類實現(xiàn)呢?通過對線性表的學(xué)習(xí),總結(jié)如下:1、線性表是數(shù)據(jù)元素的有序并且有限的集合,并且線性表中的數(shù)據(jù)元素必須是類型相同的;2、線性表可用于描述派對關(guān)系的一系列問題;3、線性表在程序中表現(xiàn)為一種特殊的數(shù)據(jù)類型;4、線性表在 C++ 中表現(xiàn)為一個抽象類。
當(dāng)前名稱:線性表的本質(zhì)、操作及順序存儲結(jié)構(gòu)(六)-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
文章起源:http://chinadenli.net/article36/eohsg.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供虛擬主機(jī)、網(wǎng)頁設(shè)計公司、品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計、電子商務(wù)、靜態(tài)網(wǎng)站、微信公眾號
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 一臺云服務(wù)器到底能干嘛? 2021-03-08
- 歐洲vps怎么樣?歐洲vps和歐洲云服務(wù)器有哪些區(qū)別? 2022-10-11
- 普通服務(wù)器和云服務(wù)器的區(qū)別嗎 2022-10-09
- 云服務(wù)器是什么?什么行業(yè)要用云服務(wù)器? 2022-10-13
- 云服務(wù)器的機(jī)房在哪 2021-02-08
- 云服務(wù)器選購一定要留意這些方面 2022-10-08
- 為什么這么多人熱衷于香港云服務(wù)器? 2021-02-19
- 什么叫云服務(wù)器,云服務(wù)器關(guān)鍵用以哪一方面? 2016-11-14
- 香港主機(jī)租用和香港云服務(wù)器哪個好? 2022-10-02
- 選擇海外云服務(wù)器,有什么側(cè)重點? 2022-10-02
- 如何選擇適合鄭州做網(wǎng)站公司的云服務(wù)器 2023-03-27
- 云服務(wù)器和傳統(tǒng)服務(wù)器哪個便宜 2021-03-03