STL容器之map與hash_map-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
一、簡(jiǎn)介

就應(yīng)用來(lái)說,map已經(jīng)是STL標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫(kù)的成員,而hash_map暫時(shí)還未進(jìn)入標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫(kù),是擴(kuò)展ext中的一個(gè)功能,但也是非常常用并且非常重要的庫(kù)。
二、簡(jiǎn)單對(duì)比
首先,要說的是這兩種數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)的都提供了KEY-VALUE的存儲(chǔ)和查找的功能。但是實(shí)現(xiàn)是不一樣的,map是用的紅黑樹,查詢時(shí)間復(fù)雜度為log(n)。而hash_map是用的哈希表,查詢時(shí)間復(fù)雜度理論上可以是常數(shù),但是消耗內(nèi)存大,是一種以存儲(chǔ)換時(shí)間的方法。
樹查找,在總查找效率上比不上hash表,但是它很穩(wěn)定,它的算法復(fù)雜度不會(huì)出現(xiàn)波動(dòng)。在一次查找中,你可以斷定它最壞的情況下其復(fù)雜度不會(huì)超過O(log2N)。而hash表就不一樣,是O(1),還是O(N),或者在其之間,你并不能把握。
三、hash_map的使用
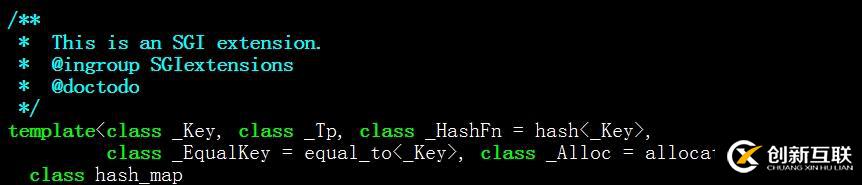
可見,如果定義完整的hash_map,需要提供<key類型,value類型,哈希函數(shù),key相等判斷函數(shù),value類型內(nèi)存分配器>等5個(gè)模板參數(shù),由于后三個(gè)都有默認(rèn)值,所以一般我們只需要提供前兩個(gè)。
1> 定義__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int> myHashMap不會(huì)出錯(cuò),然而一旦對(duì)myHashMap進(jìn)行操作,就會(huì)出現(xiàn)編譯錯(cuò)誤“instantiated from here”,這是因?yàn)間nu版本的hash_map只實(shí)現(xiàn)了有限的幾個(gè)hash模板函數(shù)(見第三個(gè)模板參數(shù),這些函數(shù)在hash_fun.h中),而這些函數(shù)里包括hash<const char*>,但是不包括hash<std::string>的實(shí)例化。解決辦法是定義哈希表前自己特化一個(gè)實(shí)例,這樣編譯器就知道調(diào)用這個(gè)函數(shù)了。
namespace __gnu_cxx
{
template <>
struct hash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string &s) const
{ return __stl_hash_string(s.c_str()); }
};
}2> 第四個(gè)參數(shù)key相等判斷函數(shù)的意義
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int> myHashMap;
char name1[10] = "zhu";
char name2[10] = "zhu";
myHashMap[name1] = 1;
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int>::iterator it = myHashMap.find(name2);
if (it == myHashMap.end())
cout << "not find" << endl;
return 0;
}你會(huì)發(fā)現(xiàn),雖然name1和name2都是zhu,但是插入了name1,用name2去查找時(shí),還是查無(wú)結(jié)果。這是涉及到第四個(gè)模板參數(shù),判斷key相等,默認(rèn)的是std::equal_to,而這個(gè)函數(shù)的定義是用operator==來(lái)進(jìn)行判斷的,指針的相等當(dāng)然就是地址一樣了,而name1和name2的地址顯然不同。解決辦法是用自己指定的函數(shù)模板替代默認(rèn)的。
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ext/hash_map>
#include <backward/hash_fun.h>
using namespace std;
template <class _Tp>
struct my_equal_to : public binary_function<_Tp, _Tp, bool>
{
bool operator()(const _Tp& __x, const _Tp& __y) const
{ return strcmp(__x, __y) == 0; }
};
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int, __gnu_cxx::hash<const char*>, my_equal_to<const char*> > myHashMap;
char name1[10] = "zhu";
char name2[10] = "zhu";
myHashMap[name1] = 1;
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int, __gnu_cxx::hash<const char*>, my_equal_to<const char*> >::iterator it = myHashMap.find(name2);
if (it == myHashMap.end())
cout << "not find" << endl;
else
cout << it->second << endl;
return 0;
}用剛剛特化的hash_map<string, int>就是可以找到的,因?yàn)閟tring重載了operator==操作符。
編譯使用-Wno-deprecated選項(xiàng),不然會(huì)有backward_warning.h頭文件里的告警。
四、膚淺的對(duì)比測(cè)試(map,系統(tǒng)hash函數(shù)的hash_map及自寫hash函數(shù)的hash_map)
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ cat /tmp/name.txt | wc -l 25848136 #從現(xiàn)有的游戲數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)里拉了561916個(gè)角色名(里面本來(lái)就有重復(fù)的),然后重復(fù)追加了幾次,變成了 #2584萬(wàn)行的數(shù)據(jù)
1.系統(tǒng)hash函數(shù)的hash_map實(shí)現(xiàn)
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
//特化hash函數(shù)的string版本
namespace __gnu_cxx
{
template <>
struct hash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string &s) const
{ return __stl_hash_string(s.c_str()); }
};
}
//計(jì)算當(dāng)前時(shí)間
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime(&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int> fileMap;
string temp; //存放每行的臨時(shí)字符串
int i = 0; //統(tǒng)計(jì)總個(gè)數(shù)
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime(); //從這里開始計(jì)時(shí)
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime(); //計(jì)時(shí)結(jié)束
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#編譯 [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ -Wno-deprecated 3.cpp -o hashMap
2.自寫hash函數(shù)的hash_map
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
struct strHash{
size_t operator()(const string& str) const
{
unsigned long __h = 0;
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < str.size() ; i ++)
__h = 107*__h + str[i];
return size_t(__h);
}
};
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime(&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int, strHash> fileMap;
string temp;
int i = 0;
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime();
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime();
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#編譯 [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ -Wno-deprecated 4.cpp -o strhashMap
3.STL的map
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime (&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
map<string, int> fileMap;
string temp;
int i = 0;
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime();
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime();
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#編譯 [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ 2.cpp -o map
4.執(zhí)行查看結(jié)果
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./hashMap #7秒 2015-11-06 16:25:41 2015-11-06 16:25:48 459256 [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./strhashMap #8秒,和上面的相差無(wú)幾 2015-11-06 16:25:50 2015-11-06 16:25:58 459256 [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./map #26秒 2015-11-06 16:26:02 2015-11-06 16:26:28 459256
五、總結(jié)
這個(gè)測(cè)試僅僅是個(gè)人娛樂,并沒有什么實(shí)際價(jià)值。最后就是一句話,hash_map是基于hash_table實(shí)現(xiàn)的,而hash_table是把以雙刃劍,用的好效率很高O(1),用的不好奔著O(N)就去了。
六、注意hash_map死循環(huán)
這個(gè)問題簡(jiǎn)單說來(lái),就是gnu的實(shí)現(xiàn)是,內(nèi)部有個(gè)_M_Cur指針指示當(dāng)前位置A,每次計(jì)算operator++,都用當(dāng)前位置的key調(diào)用hash函數(shù)計(jì)算下一個(gè)位置B,如果key傳入hash_map以后,又在外部將其內(nèi)容破壞,導(dǎo)致hash函數(shù)計(jì)算后的B位置在A位置之前,那么從B到達(dá)A以后,又會(huì)跳回B,形成B-A區(qū)間的死循環(huán)。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<char *, int> hashMap;
char name[10] = "zhu";
hashMap.insert(pair<char *, int>(name, 1));
strncpy(name, "wang", 10); //在外部改變了已經(jīng)傳入hash_map中的key,導(dǎo)致死循環(huán)
for (__gnu_cxx::hash_map<char *, int>::iterator it = hashMap.begin(); it != hashMap.end(); ++it)
{
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
}
return 0;
}另外有需要云服務(wù)器可以了解下創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)scvps.cn,海內(nèi)外云服務(wù)器15元起步,三天無(wú)理由+7*72小時(shí)售后在線,公司持有idc許可證,提供“云服務(wù)器、裸金屬服務(wù)器、高防服務(wù)器、香港服務(wù)器、美國(guó)服務(wù)器、虛擬主機(jī)、免備案服務(wù)器”等云主機(jī)租用服務(wù)以及企業(yè)上云的綜合解決方案,具有“安全穩(wěn)定、簡(jiǎn)單易用、服務(wù)可用性高、性價(jià)比高”等特點(diǎn)與優(yōu)勢(shì),專為企業(yè)上云打造定制,能夠滿足用戶豐富、多元化的應(yīng)用場(chǎng)景需求。
文章名稱:STL容器之map與hash_map-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
網(wǎng)站鏈接:http://chinadenli.net/article36/edepg.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供靜態(tài)網(wǎng)站、標(biāo)簽優(yōu)化、外貿(mào)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、搜索引擎優(yōu)化、App設(shè)計(jì)、網(wǎng)站營(yíng)銷
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請(qǐng)盡快告知,我們將會(huì)在第一時(shí)間刪除。文章觀點(diǎn)不代表本網(wǎng)站立場(chǎng),如需處理請(qǐng)聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時(shí)需注明來(lái)源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
猜你還喜歡下面的內(nèi)容
- 如何優(yōu)化JS代碼來(lái)適合網(wǎng)站優(yōu)化-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- CSS中怎么將Span標(biāo)簽設(shè)置為固定寬度-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- 附件預(yù)覽功能-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- jade模板引擎如何在Node.js中使用-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- Python3中的解釋器知識(shí)點(diǎn)整理-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- 計(jì)算機(jī)內(nèi)部用于處理數(shù)據(jù)和指令的編碼是哪個(gè)-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- 如何用CDN給網(wǎng)站加速-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 你知道響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的最大難點(diǎn)有哪些嗎? 2016-09-15
- 北京響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站建設(shè)適合哪些類型的網(wǎng)站 2023-02-26
- 響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站和手機(jī)網(wǎng)站的差別。 2019-10-03
- 響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站前端的設(shè)計(jì)尺寸標(biāo)準(zhǔn) 2016-11-08
- 告訴你響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站有哪些缺點(diǎn) 2016-09-22
- 響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站制作要考慮哪些細(xì)節(jié)因素 2016-10-04
- 響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站建設(shè)帶來(lái)哪些好處 2020-10-30
- 響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站與傳統(tǒng)網(wǎng)站制作的不同點(diǎn) 2022-07-29
- 成都網(wǎng)站制作:一個(gè)優(yōu)秀的響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站能夠給你帶來(lái)什么 2016-09-04
- 曲江響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站制作:商城式網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的顏色如何匹配? 2023-03-19
- 如何勸服客戶搭建響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站 2022-09-02
- 自適應(yīng)網(wǎng)站和響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站哪個(gè)更好有什么不同 2022-09-20