如何實現(xiàn)譯文jdk默認(rèn)hashCode方法
這篇文章主要介紹“如何實現(xiàn)譯文jdk默認(rèn)hashCode方法”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在如何實現(xiàn)譯文jdk默認(rèn)hashCode方法問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”如何實現(xiàn)譯文jdk默認(rèn)hashCode方法”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學(xué)習(xí)吧!
創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)專注于網(wǎng)站建設(shè),為客戶提供成都網(wǎng)站制作、網(wǎng)站設(shè)計、外貿(mào)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、網(wǎng)頁設(shè)計開發(fā)服務(wù),多年建網(wǎng)站服務(wù)經(jīng)驗,各類網(wǎng)站都可以開發(fā),品牌網(wǎng)站制作,公司官網(wǎng),公司展示網(wǎng)站,網(wǎng)站設(shè)計,建網(wǎng)站費用,建網(wǎng)站多少錢,價格優(yōu)惠,收費合理。
一個不起眼的小問題
上周的工作中我向一個類提交了一個微不足道的變化,實現(xiàn)toString()方法用來讓日志更有用。令我驚訝的是,變化導(dǎo)致約5%的覆蓋率下降。我知道所有新代碼都被現(xiàn)有的單元測試覆蓋,但是覆蓋率下降了,所以哪里出了問題?
對比之前的覆蓋范圍報告,一個敏銳的同事發(fā)現(xiàn),在代碼之前單元測試覆蓋了HashCode()的實現(xiàn),但改動之后就沒有覆蓋。當(dāng)然,這是對的:默認(rèn)的ToString()調(diào)用hashcode(),修改后的沒有。
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}重寫了toString之后,我們自定義的hashCode不再被調(diào)用,所以覆蓋率下降了。所有人都知道默認(rèn)的toString的實現(xiàn)原理,但是...
默認(rèn)的hashCode方法怎么實現(xiàn)的?
默認(rèn)的hashCode()返回的是唯一hash碼(identity hash code),注意這個和重寫hashCode返回的hash碼不是一個東西,如果某個類我們重寫了hashCode方法,我們還可以使用System.identityHashCode(o)來獲取它的唯一hash碼(感覺這個就是對象的身份證號)。
大家普遍認(rèn)為唯一hash碼使用的是對象內(nèi)存地址的對應(yīng)的整數(shù)(內(nèi)存整理對象移動了咋辦?),不過java api文檔是這么說的:
... is typically implemented by converting the internal address of the object into an integer, but this implementation technique is not required by the Java? programming language. 典型的實現(xiàn)方式是把對象的內(nèi)存地址轉(zhuǎn)為一個整數(shù),但是這種實現(xiàn)技術(shù)并不是java平臺必需的
鑒于JVM將重新定位對象(例如在垃圾收集期間由于晉升或壓縮),在我們計算對象的身份哈希碼之后,我們必須保留它。
默認(rèn)的hashCode實現(xiàn)
對于默認(rèn)的hashCode方法,不同的JVM可能實現(xiàn)的方式不一樣,本文只看openJDK的源碼,hashCode是native方法,入口如下:src/share/vm/prims/jvm.h 和 src/share/vm/prims/jvm.cpp
508 JVM_ENTRY(jint, JVM_IHashCode(JNIEnv* env, jobject handle))
509 JVMWrapper("JVM_IHashCode");
510 // as implemented in the classic virtual machine; return 0 if object is NULL
511 return handle == NULL ? 0 : ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode (THREAD, JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(handle)) ;
512 JVM_END然后是ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode()文件是src/share/vm/runtime/synchronizer.cpp 人們可能天真的以為方法像下面這么簡單:
if (obj.hash() == 0) {
obj.set_hash(generate_new_hash());
}
return obj.hash();但實際上有幾百行...看文件名也大概知道此處涉及到同步,也就是synchronized的實現(xiàn),是的,就是對象內(nèi)置鎖。這個隨后再討論,先看看如何生成唯一hash碼
static inline intptr_t get_next_hash(Thread* self, oop obj) {
intptr_t value = 0;
if (hashCode == 0) {
// This form uses global Park-Miller RNG.
// On MP system we'll have lots of RW access to a global, so the
// mechanism induces lots of coherency traffic.
value = os::random();
} else if (hashCode == 1) {
// This variation has the property of being stable (idempotent)
// between STW operations. This can be useful in some of the 1-0
// synchronization schemes.
intptr_t addr_bits = cast_from_oop<intptr_t>(obj) >> 3;
value = addr_bits ^ (addr_bits >> 5) ^ GVars.stw_random;
} else if (hashCode == 2) {
value = 1; // for sensitivity testing
} else if (hashCode == 3) {
value = ++GVars.hc_sequence;
} else if (hashCode == 4) {
value = cast_from_oop<intptr_t>(obj);
} else {
// Marsaglia's xor-shift scheme with thread-specific state
// This is probably the best overall implementation -- we'll
// likely make this the default in future releases.
unsigned t = self->_hashStateX;
t ^= (t << 11);
self->_hashStateX = self->_hashStateY;
self->_hashStateY = self->_hashStateZ;
self->_hashStateZ = self->_hashStateW;
unsigned v = self->_hashStateW;
v = (v ^ (v >> 19)) ^ (t ^ (t >> 8));
self->_hashStateW = v;
value = v;
}
value &= markWord::hash_mask;
if (value == 0) value = 0xBAD;
assert(value != markWord::no_hash, "invariant");
return value;
}0. A randomly generated number.隨機(jī)數(shù) 1. A function of memory address of the object.內(nèi)存地址函數(shù) 2. A hardcoded 1 (used for sensitivity testing.)硬編碼為數(shù)字1 3. A sequence.自增序列 4. The memory address of the object, cast to int.內(nèi)存地址強(qiáng)轉(zhuǎn)為int 5. Thread state combined with xorshift (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xorshift)線程狀態(tài)聯(lián)合xorshift
根據(jù)src/share/vm/runtime/globals.hpp中,生產(chǎn)環(huán)境是5,也就是xorshift,應(yīng)該也是一個隨機(jī)數(shù)方案
1127 product(intx, hashCode, 5, \ 1128 "(Unstable) select hashCode generation algorithm") \
openjdk8和9使用的是5,openjdk7和6使用的是第一種方案(也就是隨機(jī)數(shù)方案)。
對象頭與同步
在openjdk中,mark word的描述如下:細(xì)節(jié)看這里
30 // The markOop describes the header of an object. 31 // 32 // Note that the mark is not a real oop but just a word. 33 // It is placed in the oop hierarchy for historical reasons. 34 // 35 // Bit-format of an object header (most significant first, big endian layout below): 36 // 37 // 32 bits: 38 // -------- 39 // hash:25 ------------>| age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (normal object) 40 // JavaThread*:23 epoch:2 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (biased object) 41 // size:32 ------------------------------------------>| (CMS free block) 42 // PromotedObject*:29 ---------->| promo_bits:3 ----->| (CMS promoted object) 43 // 44 // 64 bits: 45 // -------- 46 // unused:25 hash:31 -->| unused:1 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (normal object) 47 // JavaThread*:54 epoch:2 unused:1 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (biased object) 48 // PromotedObject*:61 --------------------->| promo_bits:3 ----->| (CMS promoted object) 49 // size:64 ----------------------------------------------------->| (CMS free block) 50 // 51 // unused:25 hash:31 -->| cms_free:1 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (COOPs && normal object) 52 // JavaThread*:54 epoch:2 cms_free:1 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (COOPs && biased object) 53 // narrowOop:32 unused:24 cms_free:1 unused:4 promo_bits:3 ----->| (COOPs && CMS promoted object) 54 // unused:21 size:35 -->| cms_free:1 unused:7 ------------------>| (COOPs && CMS free block)
mark word格式在32和64位略有不同。后者有兩個變體,具體取決于是否啟用了壓縮對象指針。默認(rèn)情況下,Oracle和OpenJDK 8都執(zhí)行。 如果對象處于偏向鎖定狀態(tài),那么有23bit存儲的是偏向線程的指針,那么從哪里取唯一hash碼呢?
偏向鎖
對象的偏向狀態(tài)是偏向鎖導(dǎo)致的。從hotspot6開始嘗試減少給一個對象加鎖的成本。這些操作很昂貴,因為它們的實現(xiàn)通常依賴于原子CPU指令(CAS),以便在不同線程上安全地處理對象上的鎖定/解鎖請求。但是根據(jù)分析,在大多數(shù)應(yīng)用中,大部分的對象只會被一個線程鎖定,所以上述原子指令的執(zhí)行是一種浪費(cas指令已經(jīng)很快了,比上下文切換快多了,也是一種浪費。。。),為了避免這種浪費,有偏向鎖定的JVM允許線程讓對象偏向自己。如果一個對象是偏心的,那個幸運的線程加鎖和解鎖連cas指令都不需要執(zhí)行,只有沒有多個線程爭取同一個對象,偏向鎖的性能會很好。 繼續(xù)看FastHashCode:
601 intptr_t ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode (Thread * Self, oop obj) {
602 if (UseBiasedLocking) {
610 if (obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern()) {
...
617 BiasedLocking::revoke_and_rebias(hobj, false, JavaThread::current());
...
619 assert(!obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern(), "biases should be revoked by now");
620 }
621 }生成唯一hash碼時,會撤銷已存在的偏向,并且會禁用此對象的偏向能力(false意味著不要嘗試重偏向),上述代碼幾行之后,這個確實是不變的:
637 // object should remain ineligible for biased locking 638 assert (!mark->has_bias_pattern(), "invariant") ;
這意味著請求一個對象的唯一hash碼會禁用這個對象的偏向鎖,嘗試鎖定此對象需要使用昂貴的原子指令,即使只有一個線程請求鎖。
為什么偏向鎖和唯一hash碼有沖突?
要回答這個問題,我們必須了解哪些是標(biāo)記字的可能位置,具體取決于對象的鎖定狀態(tài)。從HotSpot Wiki的示例圖中有如下轉(zhuǎn)換: 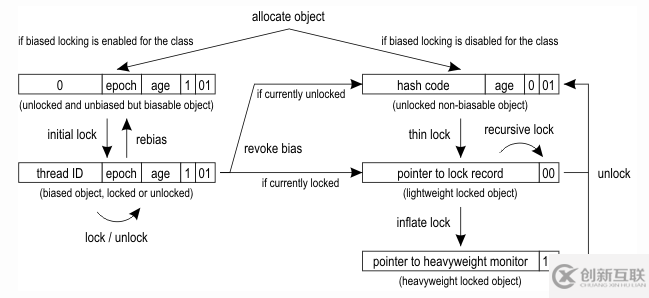
到此,關(guān)于“如何實現(xiàn)譯文jdk默認(rèn)hashCode方法”的學(xué)習(xí)就結(jié)束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學(xué)習(xí),快去試試吧!若想繼續(xù)學(xué)習(xí)更多相關(guān)知識,請繼續(xù)關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)網(wǎng)站,小編會繼續(xù)努力為大家?guī)砀鄬嵱玫奈恼拢?/p>
新聞名稱:如何實現(xiàn)譯文jdk默認(rèn)hashCode方法
當(dāng)前鏈接:http://chinadenli.net/article32/ghocsc.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供自適應(yīng)網(wǎng)站、網(wǎng)站營銷、品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計、搜索引擎優(yōu)化、網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航、網(wǎng)頁設(shè)計公司
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 專業(yè)的APP設(shè)計師告訴你,怎么做可以讓APP更“快”! 2016-11-11
- 移動APP設(shè)計中字體排版有何技巧? 2016-08-16
- APP設(shè)計之--導(dǎo)航 2022-06-22
- APP設(shè)計開發(fā)中產(chǎn)品經(jīng)理崗位有什么重要作用 2020-12-09
- 大勢所趨!十大令人振奮的移動端APP設(shè)計趨勢 2022-06-13
- app設(shè)計技巧:國外大師教你四步設(shè)計框架 2022-05-29
- 動效-APP設(shè)計的肢體語言 2022-06-30
- 淺析電商APP設(shè)計應(yīng)該注意的問題? 2016-10-11
- APP開發(fā)過程中用戶體驗設(shè)計需考慮的9大原則 2023-03-04
- 成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)情況下的APP設(shè)計3如何處理加載頁面? 2013-11-28
- APP設(shè)計易用性的七個要素 2022-06-20
- 網(wǎng)頁APP設(shè)計與用戶體驗中的同情心與同理心 2021-06-01