Android中怎么利用Layout實(shí)現(xiàn)用戶界面-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
今天就跟大家聊聊有關(guān)Android中怎么利用Layout實(shí)現(xiàn)用戶界面,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結(jié)了以下內(nèi)容,希望大家根據(jù)這篇文章可以有所收獲。
創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)建站主營(yíng)寶應(yīng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的網(wǎng)絡(luò)公司,主營(yíng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)方案,APP應(yīng)用開(kāi)發(fā),寶應(yīng)h5微信小程序搭建,寶應(yīng)網(wǎng)站營(yíng)銷推廣歡迎寶應(yīng)等地區(qū)企業(yè)咨詢1.幀布局 FrameLayout:
FrameLayout是最簡(jiǎn)單的布局對(duì)象。在它里面的的所有顯示對(duì)象都將固定在屏幕的左上角,不能指定位置,后一個(gè)會(huì)直接覆蓋在前一個(gè)之上顯示:
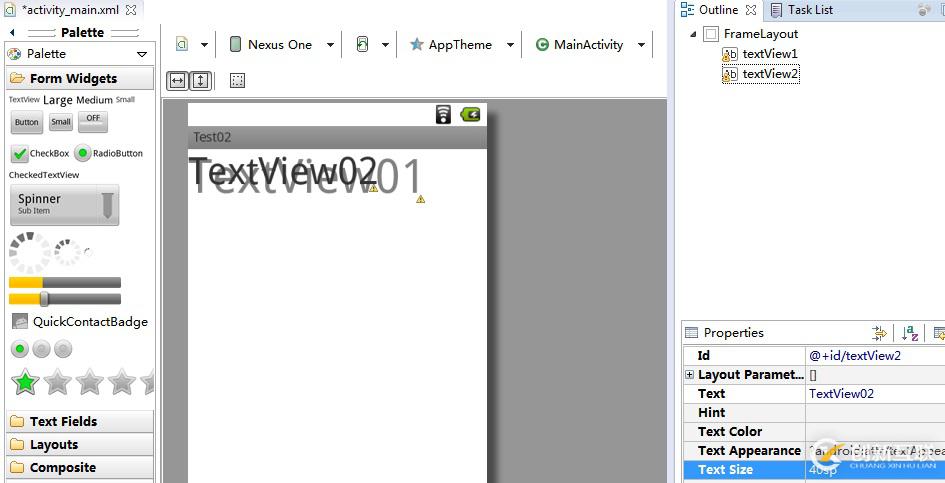
如圖所示第二個(gè)TextView直接覆蓋在了第一個(gè)TextView上面。
2.線性布局 LinearLayout:
LinearLayout是最常用的布局之一,也是RadioGroup, TabWidget, TableLayout, TableRow, ZoomControls類的父類,它里面所有顯示的對(duì)象都以垂直或水平的方式排列(通過(guò)設(shè)置LinearLayout的Orentation屬性來(lái)設(shè)置排列方式):

3.相對(duì)布局 RelativeLayout:
RelativeLayout 允許子元素指定它們相對(duì)于其父元素或兄弟元素的位置,是實(shí)際布局中最常用的布局方式之一。它靈活性大、屬性也多,操作難度比較大,屬性之間產(chǎn)生沖突的的可能性也大,使用相對(duì)布局時(shí)需要多做測(cè)試。

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/imageView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:src="@drawable/test" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/imageView1" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:text="在imageView1下方" android:textSize="15sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/textView1" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:text="在testView1下方" android:textSize="15sp" /> </RelativeLayout>
RelativeLayout用到的一些重要的屬性:
第一類:屬性值為true或false
android:layout_centerHrizontal -------------------------------水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical ---------------------------------垂直居中
android:layout_centerInparent --------------------------------相對(duì)于父元素完全居中
android:layout_alignParentBottom ----------------------------貼緊父元素的下邊緣
android:layout_alignParentLeft --------------------------------貼緊父元素的左邊緣
android:layout_alignParentRight ------------------------------貼緊父元素的右邊緣
android:layout_alignParentTop --------------------------------貼緊父元素的上邊緣
android:layout_alignWithParentIfMissing ----------------------如果對(duì)應(yīng)的兄弟元素找不到的話就以父元素做參照物
第二類:屬性值必須為id的引用名“@id/id-name”
android:layout_below -----------------------------------------在某元素的下方
android:layout_above ----------------------------------------在某元素的的上方
android:layout_toLeftOf --------------------------------------在某元素的左邊
android:layout_toRightOf -------------------------------------在某元素的右邊
android:layout_alignTop --------------------------------------本元素的上邊緣和某元素的的上邊緣對(duì)齊
android:layout_alignLeft --------------------------------------本元素的左邊緣和某元素的的左邊緣對(duì)齊
android:layout_alignBottom ----------------------------------本元素的下邊緣和某元素的的下邊緣對(duì)齊
android:layout_alignRight -------------------------------------本元素的右邊緣和某元素的的右邊緣對(duì)齊
第三類:屬性值為具體的像素值,如30dip,40px
android:layout_marginBottom --------------------------------離某元素底邊緣的距離
android:layout_marginLeft ------------------------------------離某元素左邊緣的距離
android:layout_marginRight ----------------------------------離某元素右邊緣的距離
android:layout_marginTop ------------------------------------離某元素上邊緣的距離
4.表格布局 TableLayout:
TableLayout以行列的形式管理子元素,每一行是一個(gè)TableRow布局對(duì)象,當(dāng)然也可以是普通的View對(duì)象,TableRow離每放一個(gè)元素就是一列,總列數(shù)由列數(shù)最多的那一行決定。

<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:stretchColumns="*" > <TableRow android:id="@+id/tableRow1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:layout_span="2" android:text="第一行合并兩列居中" android:textSize="20sp" /> </TableRow> <TableRow android:id="@+id/tableRow2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第一行第一列" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第一行第二列" /> </TableRow> <TableRow android:id="@+id/tableRow3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第二行第一列" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第二行第二列" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
android:layout_span="2"是設(shè)置該TextView占據(jù)2列(我在界面設(shè)計(jì)器里面沒(méi)找到TextView的Span屬性,所以是在xml文件里面直接添加的),android:stretchColumns="*"是設(shè)置該TableLayout的所有列都自動(dòng)擴(kuò)展,如果不設(shè)置自動(dòng)擴(kuò)展每行列寬會(huì)根據(jù)顯示的內(nèi)容改變。

TableLayout的幾個(gè)重要屬性:
collapseColumns -----------------------------設(shè)置隱藏那些列,列ID從0開(kāi)始,多個(gè)列的話用”,”分隔
stretchColumns ------------------------------設(shè)置自動(dòng)伸展那些列,列ID從0開(kāi)始,多個(gè)列的話用”,”分隔
shrinkColumns -------------------------------設(shè)置自動(dòng)收縮那些列,列ID從0開(kāi)始,多個(gè)列的話用”,”分隔
看完上述內(nèi)容,你們對(duì)Android中怎么利用Layout實(shí)現(xiàn)用戶界面有進(jìn)一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識(shí)或者相關(guān)內(nèi)容,請(qǐng)關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)-成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司行業(yè)資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
分享標(biāo)題:Android中怎么利用Layout實(shí)現(xiàn)用戶界面-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
轉(zhuǎn)載源于:http://chinadenli.net/article24/cdosce.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供網(wǎng)站制作、響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站、網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)、做網(wǎng)站、建站公司、App設(shè)計(jì)
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請(qǐng)盡快告知,我們將會(huì)在第一時(shí)間刪除。文章觀點(diǎn)不代表本網(wǎng)站立場(chǎng),如需處理請(qǐng)聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時(shí)需注明來(lái)源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
猜你還喜歡下面的內(nèi)容

移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)知識(shí)
- 成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè):移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)要點(diǎn)分享! 2016-11-08
- 移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)中不可或缺的四大要素 2016-11-04
- 移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)必備的基本常識(shí) 2016-11-16
- 淺析移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)要注意哪些細(xì)節(jié) 2016-11-04
- 移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)在設(shè)計(jì)上應(yīng)該注意哪些? 2022-06-06
- 移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)關(guān)注移動(dòng)支付花樣百出,為此誰(shuí)get了? 2022-07-14
- 智能手機(jī)與移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的關(guān)系 2023-02-20
- 移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)有什么作用? 2016-11-07
- 移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的核心內(nèi)容是什么 2021-09-26
- 移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)與電腦端網(wǎng)站建設(shè)有何不同?應(yīng)如何提高用戶體驗(yàn)? 2022-10-28
- 網(wǎng)絡(luò)時(shí)代的新發(fā)展——移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè) 2016-11-07
- 如何做好移動(dòng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)中的用戶體驗(yàn)工作 2022-08-22